Releasing Damn Vulnerable iOS App v2.0 - written in Swift
I am glad to release a completely new version of Damn Vulnerable iOS App written in Swift 4. With developers now migrating to Swift for developing apps, it is important to have a testbed app for iOS in Swift. Though I have added some sections in Objective-C too which the users can test to learn Objective-C related vulns.
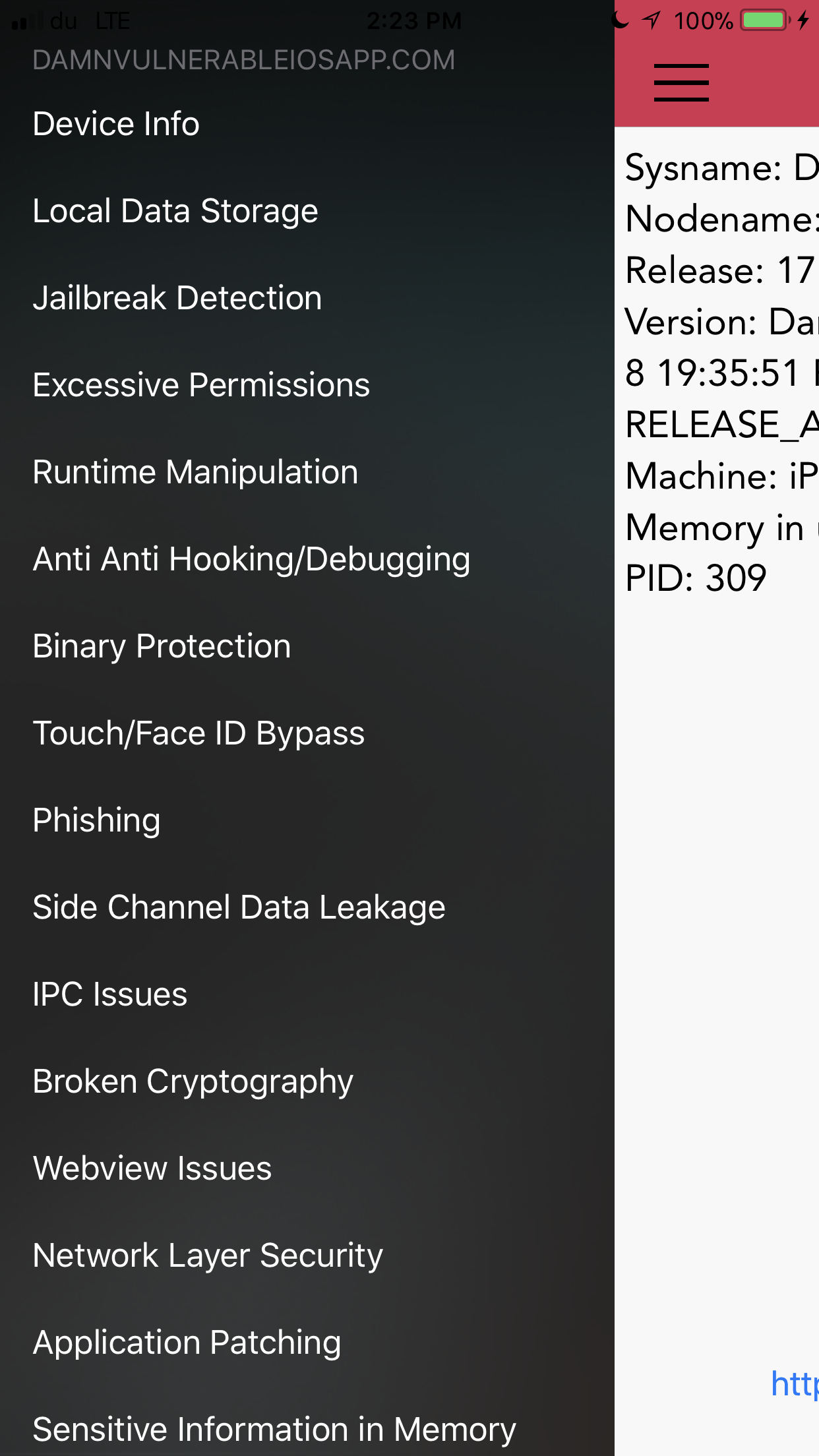
The following vulnerabilities are covered in this version.
- Local Data Storage - Data Storage in Plist, UserDefaults, Keychain, CoreData, Webkit Cache, Realm, Couchbase and YapDatabase.
- Jailbreak Detection - 5 challenges in this section. Apart from the usual checks where you can use runtime manipulation and attach debuggers to bypass Jailbreak detection, users will have to mitigate scenarios where there is added runtime protection, use of inline functions, string obfuscation, and certain edge cases, for e.g the exiting of an app when a jailbroken device is detected.
- Excessive Permissions - A demo on how app permissions can be misused, as demonstrated by Krause originally.
- Runtime Manipulation - Use runtime manipulation to modify instance variables, bypass local login checks, and brute force pin codes. In some cases, you might have to attach a debugger.
- Anti Anti Hooking/Debugging - Enabling these will detect when a debugger or a runtime analysis tool such as Cycript is attached to the app. There is also detection for MobileSubstrate, SSLKillSwitch2 etc. Try and work your way around it and see if you can still solve other challenges with these limitations. Reverse & Patch, Patch, Patch !
- Binary Protection - Do some binary analysis to identify whether ARC, PIE, Stack smashing is enabled. Find the signature used to sign the binary and the entitlements it has. Also check if the app is stripped of its symbols or not.
- Touch/Face ID Bypass - Bypass Touch ID authentication when insecure APIs (LAContext) are being used.
- Phishing - Demonstration of alerts generated by app that look like the ones generated from App Store, which can potentially be used for conducting phishing attacks. Original idea by Krause.
- Side Channel Data Leakage - Understand the different kinds of Side Channel Data leakage such as Device Logs, Pasteboard, App Screenshot, Keystroke Logging, Insecure APIs used for HTTP Cookies etc.
- IPC Issues - Solve this challenge to understand what can happen when an app is receiving requests via URL schemes from untrusted sources and doesn’t validate it properly.
- Broken Cryptography - Bypass 2 encryption and hashing implementations, one with AES and the other one with PBKDF2 with only few rounds of hashing.
- Webview Issues - Understand injections in Webviews.
- Network Layer Security - Capture traffic over HTTP and HTTPs. Bypass Certificate and Public Key Pinning. Also understand what is ATS (App Transport Security) and check whether it is implemented or not.
- Application Patching - Patch login checks, jailbreak detection methods, and in specific certain specific instructions used in the app.
- Sensitive Information in Memory - Dump the information from the memory to look at the sensitive data.
- Data leakage to third parties - Identify and Capture the data being leaked to third parties.